Use cases
Common use cases for the refresh token exchange include:- Web application: A web-based productivity app connects to a user’s Google Calendar and performs tasks on the user’s behalf, such as scheduling meetings, without requiring the user to re-authenticate.
- Mobile application: A mobile photo gallery app connects to a user’s Google Photos account and uploads photos as they’re taken, keeping the user logged in by refreshing the access token in the background.
How it works
The following sequence diagram describes end-to-end how to call external APIs using the refresh token exchange in Auth0: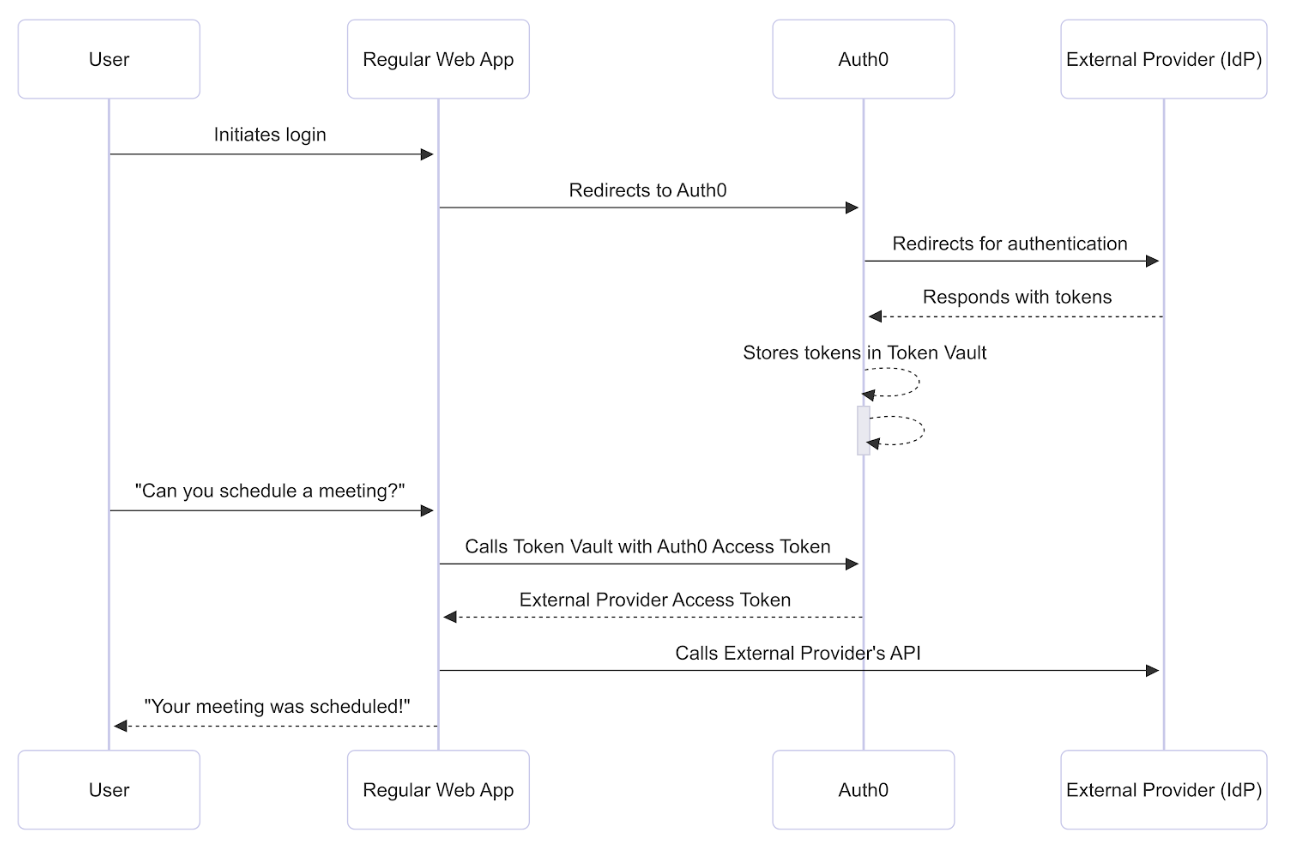
Prerequisites
Before getting started, you must configure the refresh token exchange with Token Vault.Step 1: Connect and authorize access
To schedule the meeting, the web application needs to connect with Google via Auth0 and then receive the user’s permission to access the Google Calendar API. The user logs into the application via Google with the Connected Accounts flow, which uses the My Account API. After the My Account API validates and completes the Connected Accounts request, it stores the Google access and refresh tokens with the requested calendar scopes in the Token Vault.Step 2: Perform refresh token exchange
While Token Vault does not support refresh token rotation, you can use DPoP to bind Auth0-issued tokens to your client for additional security. To successfully perform the refresh token exchange with Token Vault, disable Allow Refresh Token Rotation for your application in the Auth0 Dashboard.
POST request to the /oauth/token endpoint with the following parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
grant_type | The grant type. For Token Vault, set to urn:auth0:params:oauth:grant-type:token-exchange:federated-connection-access-token |
client_id | Client application ID |
client_secret | Client secret. Note: You can use any client authentication method to get an external provider’s access token. |
subject_token_type | Type of subject token. For Token Vault, set to refresh token: urn:ietf:params:oauth:token-type:refresh_token |
subject_token | The Auth0 refresh token that the Auth0 Authorization Server validates to identify the user. |
requested_token_type | The requested token type. For Token Vault, set to the external provider’s access token or http://auth0.com/oauth/token-type/federated-connection-access-token |
connection | The connection name, in this case, google-oauth2. |
login_hint | (Optional) Only use login_hint if the user has several accounts from the same connection, such as a work Google account and personal Google account. When you pass in a value for the login_hint during the token exchange, you are explicitly identifying which of the user’s multiple linked accounts the request is for. |
Step 3: Auth0 Authorization Server validates refresh token
The Auth0 Authorization Server validates and loads the user profile associated with the Auth0 refresh token:- Auth0 checks if the user profile’s
connected_accountsarray contains a user account with the connection name passed in the authorization request. - If the authorization request contains
login_hint, Auth0 looks for an identity matching both the connection name and thelogin_hint. - If Auth0 can’t find the user, it returns a
401status code with an error message.

