By Damien Guard
This tutorial demonstrates how to add authorization to an ASP.NET OWIN API using the standard JWT middleware.We recommend that you log in to follow this quickstart with examples configured for your account.New to Auth0? Learn how Auth0 works and read about implementing API authentication and authorization using the OAuth 2.0 framework.
Configure Auth0 APIs
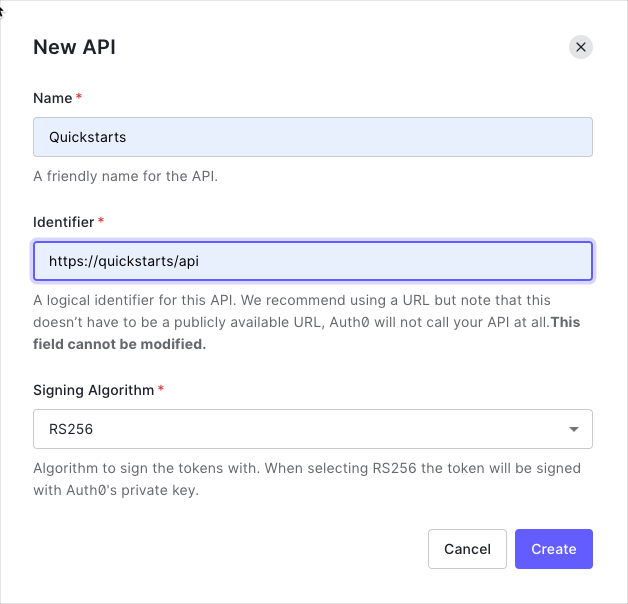
Create an API
In the APIs section of the Auth0 dashboard, click Create API. Provide a name and an identifier for your API, for example,https://quickstarts/api. You will use the identifier as an audience later, when you are configuring the Access Token verification. Leave the Signing Algorithm as RS256.
Define permissions
Permissions let you define how resources can be accessed on behalf of the user with a given access token. For example, you might choose to grant read access to themessages resource if users have the manager access level, and a write access to that resource if they have the administrator access level.
You can define allowed permissions in the Permissions view of the Auth0 Dashboard’s APIs section.
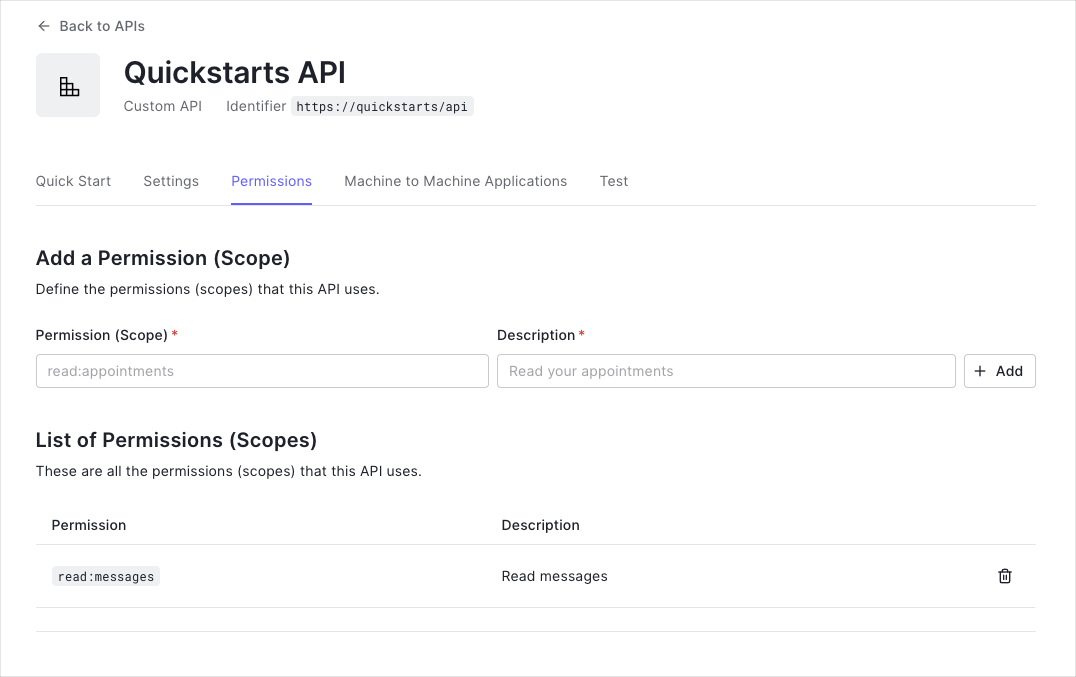
This example uses the
read:messages scope.- How to check for a JSON Web Token (JWT) in the
Authorizationheader of an incoming HTTP request. - How to check if the token is valid, using the JSON Web Key Set (JWKS) for your Auth0 account. To learn more about validating Access Tokens, see Validate Access Tokens.
Configure the Sample Project
The sample code has anappsettings section in Web.config which configures it to use the correct Auth0 Domain and API Identifier for your API. If you download the code from this page it will be automatically filled. If you use the example from Github, you will need to fill it yourself.
Validate Access Tokens
Install dependencies
To use Auth0 Access Tokens with ASP.NET you will use the OWIN JWT Middleware which is available in theMicrosoft.Owin.Security.Jwt NuGet package.
Verifying the token signature
As the OWIN JWT middleware doesn’t use Open ID Connect Discovery by default, you will need to provide a customIssuerSigningKeyResolver. To do this, add the following to the Support/OpenIdConnectSigningKeyResolver.cs file:
Such a custom resolver was previously published as part of the
Auth0.OpenIdConnectSigningKeyResolver package through Nuget. As this package is not available anymore, you will need to provide this yourself.OpenIdConnectSigningKeyResolver will automatically download the JSON Web Key Set used to sign the RS256 tokens from the OpenID Connect Configuration endpoint (at /.well-known/openid-configuration). You can then use it subsequently to resolve the Issuer Signing Key, as will be demonstrated in the JWT registration code below.
Configuration
Go to theConfiguration method of your Startup class and add a call to UseJwtBearerAuthentication passing in the configured JwtBearerAuthenticationOptions.
The JwtBearerAuthenticationOptions needs to specify your Auth0 API Identifier in the ValidAudience property, and the full path to your Auth0 domain as the ValidIssuer. You will need to configure the IssuerSigningKeyResolver to use the instance of OpenIdConnectSigningKeyResolver to resolve the signing key:
Validate scopes
The JWT middleware above verifies that the Access Token included in the request is valid; however, it doesn’t yet include any mechanism for checking that the token has the sufficient scope to access the requested resources. Create a class calledScopeAuthorizeAttribute which inherits from System.Web.Http.AuthorizeAttribute. This Authorization Attribute will check that the scope claim issued by your Auth0 tenant is present, and if so it will ensure that the scope claim contains the requested scope.
Protect API Endpoints
The routes shown below are available for the following requests:GET /api/public: available for non-authenticated requestsGET /api/private: available for authenticated requests containing an access token with no additional scopesGET /api/private-scoped: available for authenticated requests containing an access token with theread:messagesscope granted
[Authorize] attribute to secure an endpoint.
ScopeAuthorize attribute and pass the name of the required scope in the scope parameter.

