このガイドは、新規または既存のExpress.js APIアプリケーションに
express-oauth2-jwt-bearerパッケージを使ってAuth0を統合する方法を説明します。Auth0 DashboardでAPIをまだ作成していない場合は、対話型のセレクターを使ってAuth0 APIを新規作成します。そうでない場合は、既存のプロジェクトAPIを選択します。Auth0 Dashboardを使って初めてAPIをセットアップする場合には、使用の開始ガイドを確認してください。それぞれのAuth0 APIにはAPI識別子があり、アプリケーションにアクセストークンの検証で使用されます。Auth0を初めてご利用ですか? Auth0の仕組みと、OAuth 2.0フレームワークを用いたAPI認証と認可の実装について説明します。
アクセス許可は、ユーザーの代わりに、提供されたアクセストークンを使ってどのようにしてリソースにアクセスできるのかを定義できるようにします。たとえば、ユーザーがマネージャーアクセスレベルを持つ場合には、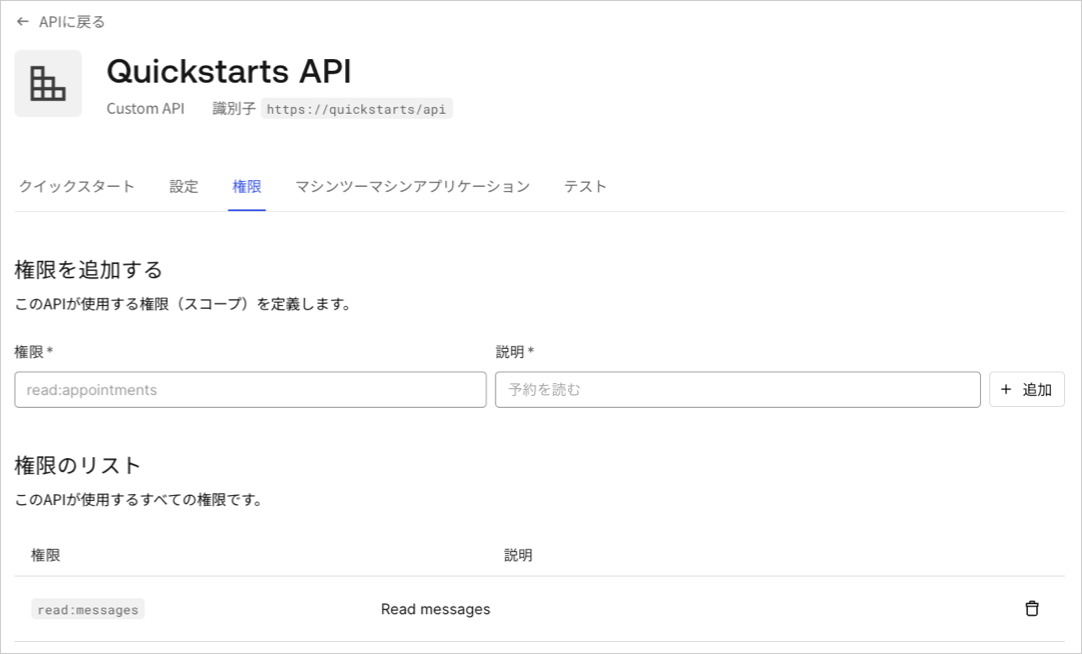
messagesリソースに対して読み出しアクセスを付与し、管理者アクセスレベルを持つ場合には、書き込みアクセスを付与することができます。Auth0 Dashboardの[APIs]セクションにある**[Permissions(権限)]** ビューで使用可能なアクセス許可を定義することができます。
以下の例では
read:messagesスコープを使用します。有効なJWTを必須して個々のルートを保護するには、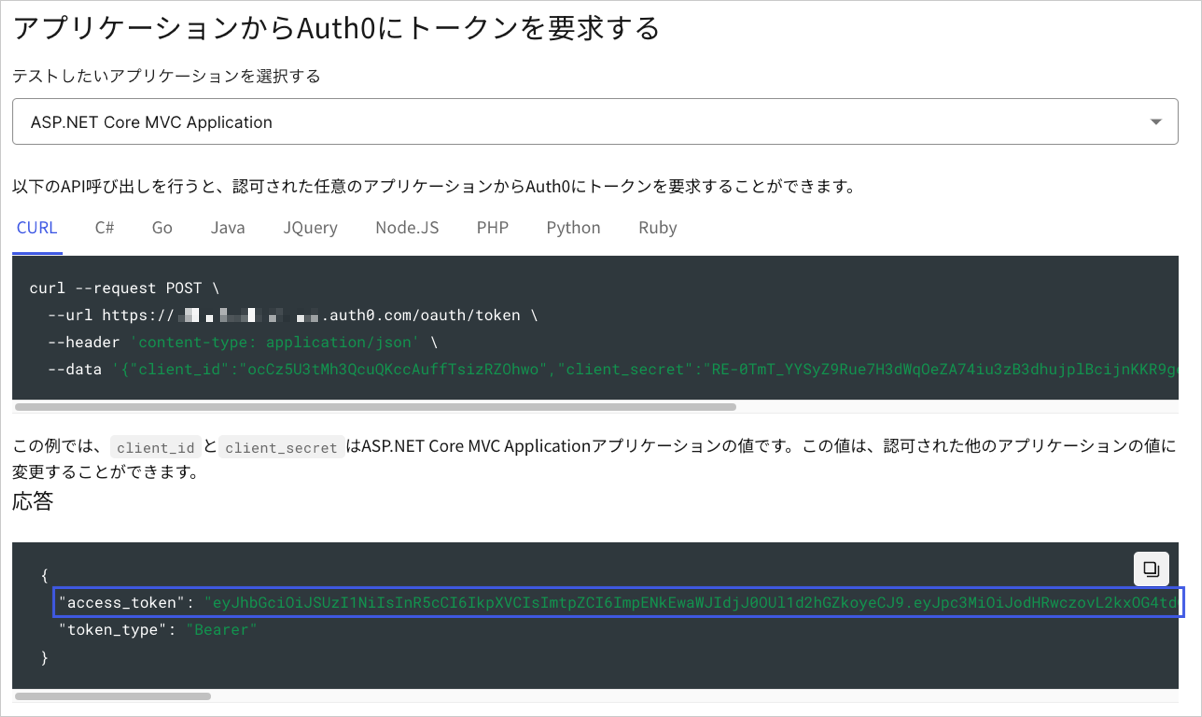 要求の
要求の
express-oauth2-jwt-bearerから構築されたcheckJwtミドルウェアでルートを構成します。特定のスコープを検索するために、個々のルートを構成することができます。これを実現するには、requiresScopeメソッドで別のミドルウェアをセットアップします。必要なスコープを提供し、認可を追加したいルートにミドルウェアを適用します。checkJwtとrequiredScopesミドルウェアを保護したいルートに渡します。この構成では、read:messagesスコープを持つアクセストークンのみがエンドポイントにアクセスすることができます。APIを呼び出す
APIを呼び出すにはアクセストークンが必要です。テスト用のアクセストークンは、API設定の**[Test(テスト)]** ビューから取得することができます。
Authorizationヘッダーにアクセストークンを指定します。チェックポイント
アプリケーションの構成が完了したら、アプリケーションを実行して次の点を確認します: GET /api/publicが認証を必要としない要求に使用できる。 GET /api/privateが認証された要求に使用できる。 GET /api/private-scopedがread:messagesスコープが付与されたアクセストークンを含む認証された要求に使用できる。次のステップ
成功です!ここまで来れば、アプリケーションにログイン、ログアウト、ユーザープロファイル情報が備わっているはずです。これでクイックスタートチュートリアルは終了ですが、機能はまだまだたくさんあります。Auth0でできることについて詳しくは、以下をご覧ください。- Auth0 Dashboard - Auth0のテナントやアプリケーションを構成して管理する方法について説明します
- express-oauth2-jwt-bearer SDK - このチュートリアルで使用されているSDKをより詳しく説明します
- Auth0 Marketplace - Auth0の機能性を拡張できる各種の統合を見つけられます

