By Luciano Balmaceda
This document will help you troubleshoot your configuration if you get unexpected responses from your API.We recommend that you log in to follow this quickstart with examples configured for your account. If you configured JWT validation correctly, you will be able to get proper responses from your API when you make requests. However, in the case where you get a 401 (Unauthorized) response from your API, it is because the configuration of your JWT middleware does not match with the JWT which was passed. This document will help you troubleshoot your JWT middleware configuration.How Does a Token Get Validated?
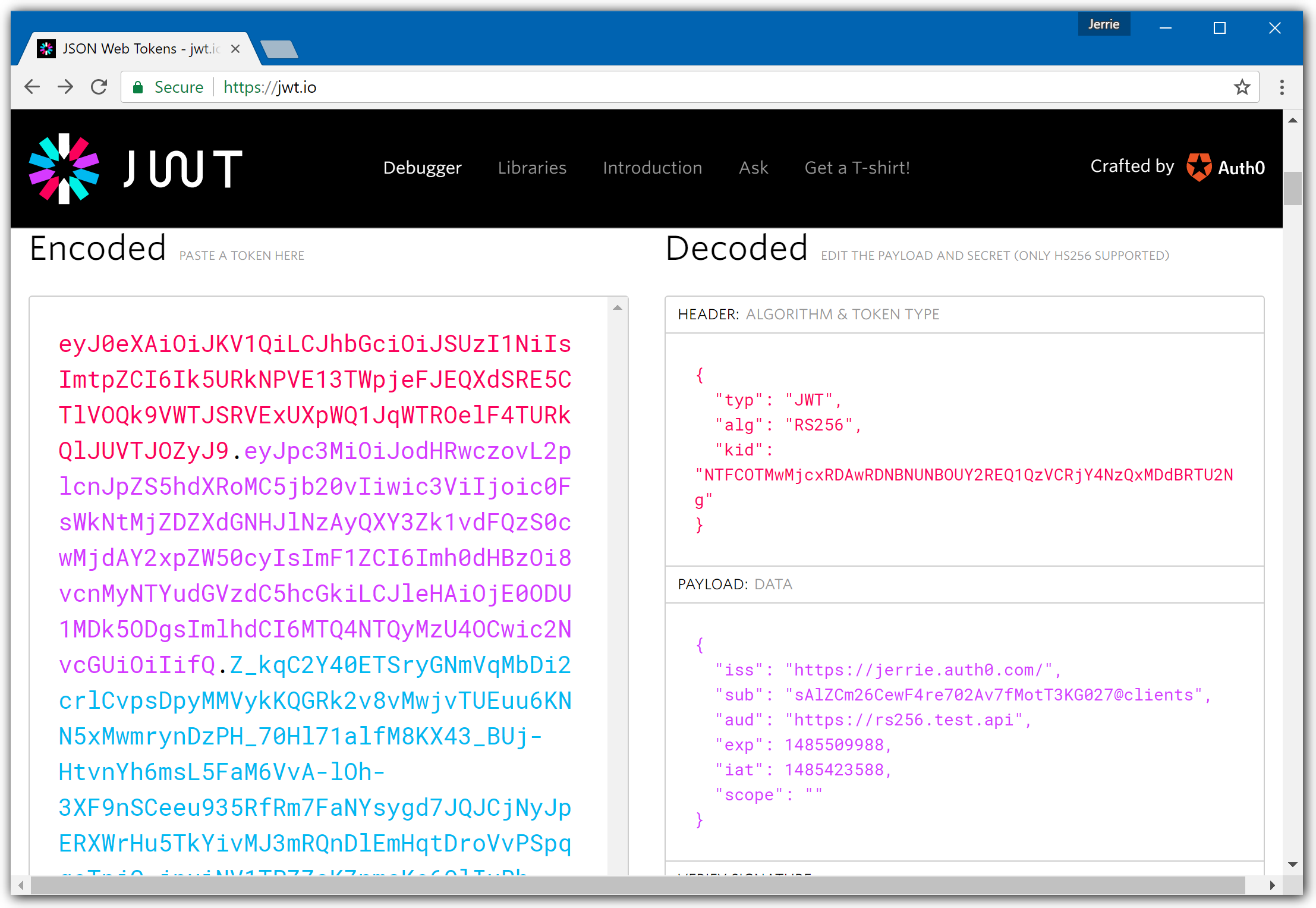
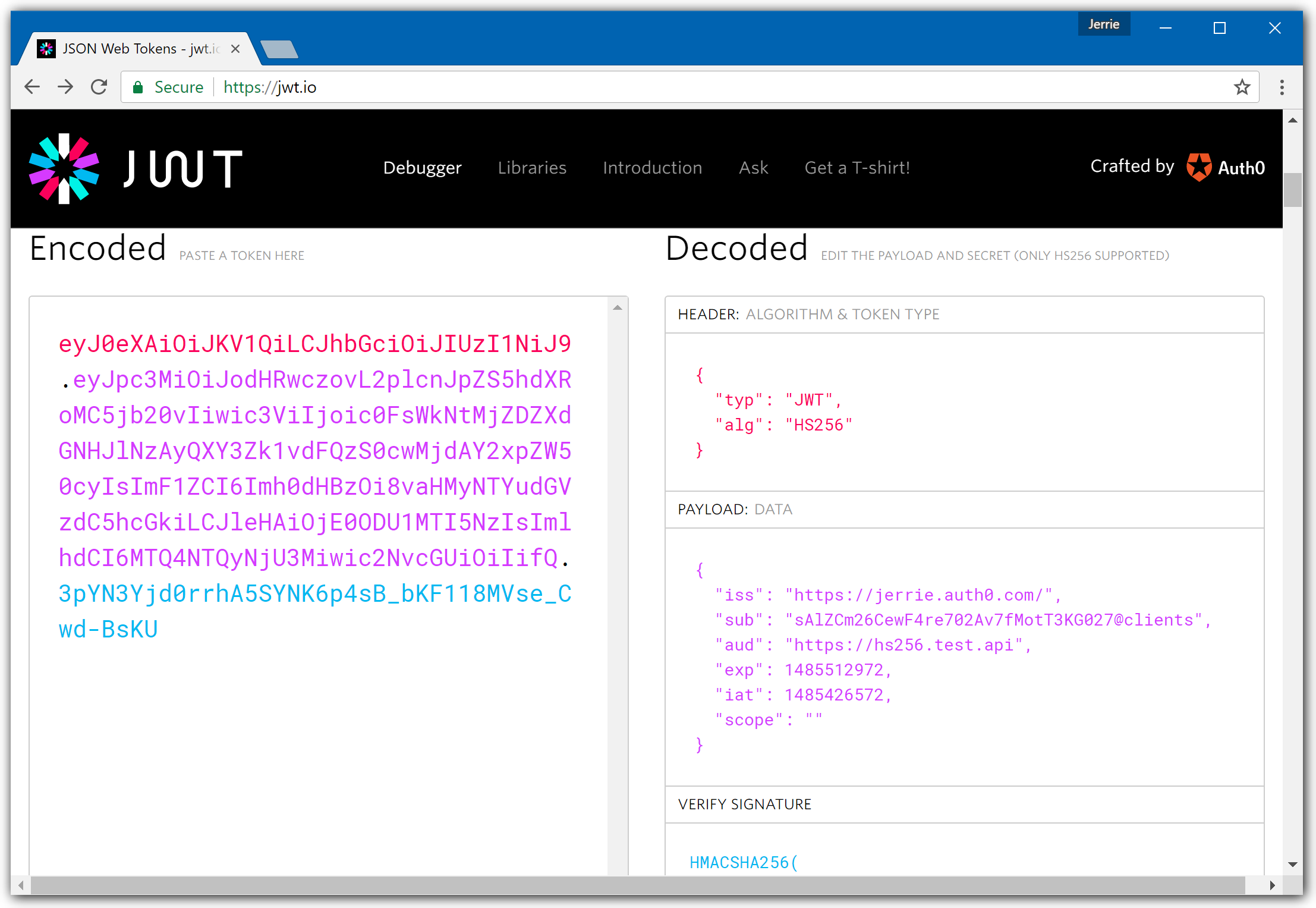
In terms of validating a JWT, there are various things to consider:- Is the token well-formed? In other words, is this token conforming to the structure of a JSON Web Token (JWT)? To get more information on the structure of a JWT, please refer to this section on the structure of a JWT
- Has the token been tampered with? The last part of a JWT is the signature. The signature is used to verify that the token was in fact signed by the sender and not altered in any way.
-
Has the token been received in its validity period? JWTs are only valid for a specified time period (as expressed in the
expclaim). -
Is the token coming from the intended Authority? This consists of 2 parts
- Signature Verification: Can we confirm that the JWT is correctly signed using the key issued by the issuing authority?
- Issuer Value: The Issuer is defined in the
issclaim. Once again does this claim match up with what your application expects?
-
Is the token intended for the current application? So does the
audclaim of the JWT match with what your application is expecting?
Inspecting a Token
A quick way to inspect a JWT is by using the JWT.io website. It has a handy debugger which allows you to quickly check that a JWT is well-formed, and also inspect the values of the various claims.