In 2017, nearly 179 million records were exposed due to data breaches. It's clear that cyber criminals are growing more creative with how they gain access to networks and valuable data.
Many of today’s most common cyberattacks have been socially engineered to rely on human error. Even your best employees can become your greatest weakness if they open a suspicious email, click on a malicious link, or pick up and use an anonymous USB device.
There are ways to protect your organization against sensitive data breaches. Here are four of the most common cyberattack examples and the ways you can avoid them.
1. Malware Infiltration
What makes you vulnerable: outdated software and lack of backup protocols
Malware is a term that encompasses many different types of malicious software, including ransomware and spyware. Each type of malware can wreak havoc once it gains access to a system.
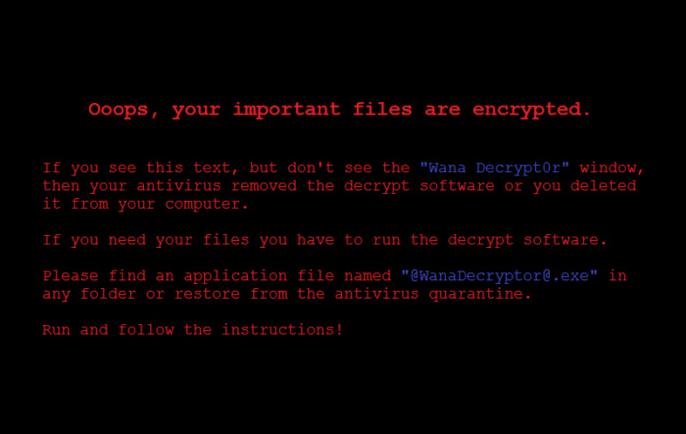
WannaCry, for example, a form of ransomware, recently took advantage of a weak spot in Microsoft’s operating system. Banks, health care providers, manufacturers, and other businesses across the globe reported WannaCry's encryption.
[Source]
In order to regain access to their computers, along with any files that hadn’t been backed up, businesses had to pay a ransom to the creators of the WannaCry program in bitcoin. Sixteen National Health Service’s offices and over 200,000 PCs worldwide reported this.
Solution: Regularly updating your systems will go a long way toward removing dangerous holes. It's a simple fix that many teams, including Equifax, have neglected.
If you want added security, consider moving to the cloud. Not only will this allow your enterprise more flexibility to scale, but you can also delegate specialized security tasks like IAM and encryption to expert providers.
2. Phishing
What makes you vulnerable: lack of education and attention to detail in suspicious e-mails
In 2016, 91% of cyberattacks were the result of a spear-phishing email. Phishing e-mails steal data either by tricking recipients into giving it to the cyber criminals or by getting users to download a file that installs spyware—software designed to steal information directly from a user’s device.
Children’s Mercy Hospital recently reported a breach that exposed the health care information of at least 60,000 people. E-mails tricked users into disclosing their work e-mail credentials, which led to the exposure of patient health data when the hackers gained access to the inboxes of the targeted hospital workers. Children’s Mercy is now being sued for this major breach.
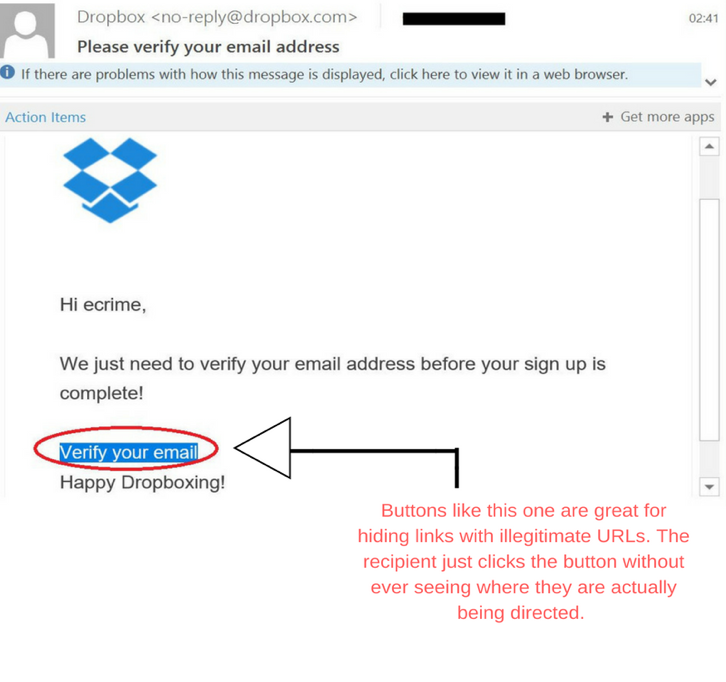
Here’s an example of an imitation Dropbox e-mail asking for confirmation of a user’s e-mail:
When users click the “Verify your email” link, spyware software is automatically downloaded onto the users' computers.
Solution: As these e-mails start to look more realistic, it’s important to educate employees on how to spot a questionable e-mail chain.
Creative training programs include the following:
- Digital Defense's SecurED training program that works with award-winning Hollywood comedy writers
- Terranova's customizable newsletters
- Inspired eLearning's Security Awareness for the C-Suite
- Wombat Security's everyday tips
3. USB Traps
What makes you vulnerable: lack of education and policy on outside device use
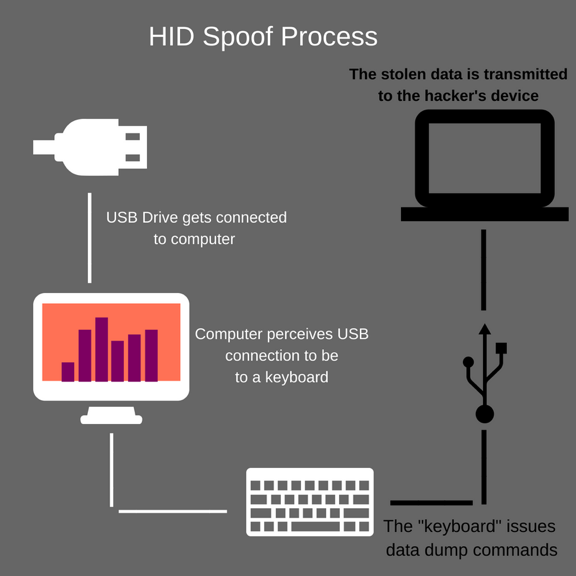
Hackers who want a direct route to company data often use a hardware device, such as a USB drive. A recent Google study revealed that at least 45% of people who find a USB drive will plug it into their computers. Planted USB drives may contain malware or a link that requests information, similar to a phishing e-mail.
The worst-case scenario is a drive that contains a HID spoof. This is where the USB drive tricks the computer into believing the drive is actually a keyboard and then issues a set of keystrokes that forces the computer to dump data back to the hacker. It can also allow them access to whatever network the computer is connected to.
Solution: Outlawing anonymous, external drives on company devices will send a clear message to your organization. Whether a drive was planted or simply purchased from an illegitimate source, removing the temptation to plug something in without properly vetting is a low-hanging fruit that can have enormous power to secure your team and your end users.
4. Mobile Attacks
What makes you vulnerable: employees accessing company data and networks via cell phones
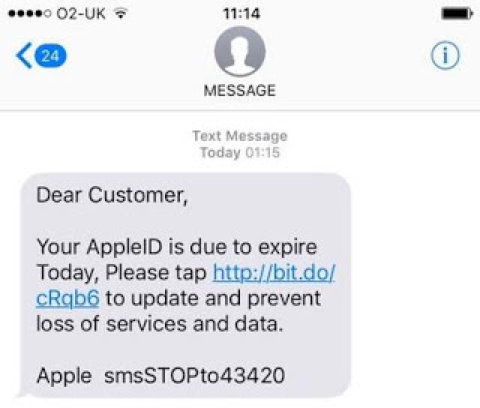
Hackers are well aware of the explosion of smartphone and tablet use and have created attacks specifically designed for mobile software. The Pegasus attack on Apple’s iOS software is a prime example. Pegasus infected iPhones through phishing text messages that asked recipients to click on a link inside the text message.
Phishing text messages are composed to look legitimate, just as phishing e-mails are. With Pegasus, clicking the link triggered the installation of spyware capable of monitoring people through their camera and microphone. The software also copied all of their calendar, contact, and e-mail data.
Pegasus was an especially frightening cyberattack because it took advantage of “zero day” vulnerabilities, meaning there wasn’t any prior knowledge of the vulnerabilities in Apple’s iOS until Pegasus struck. Once infected, users had their login credentials stolen from WhatsApp, Gmail, and other sensitive communication applications.
Solution: If a mobile phone or tablet has been breached, you need a Plan B. Make sure employees quickly change their passwords by using a professional password manager, such as LastPass or Valt. Many employees secure critical information with easy-to-guess iterations of a single password. Encouraging length and complexity in all passwords going forward will make it difficult for hackers to access multiple areas at once.
Additional Security for All Systems at the Login Stage
Good password policy and sound employee education are key; however, taking the next step with secure login procedures will add a new dimension of safety to your system. Specialized identity solutions providers can offer support with multifactor authentication.
Tracking your users from the start will help eliminate fraud at its origin, helping provide a secure foundation to allow your team to scale.
About Auth0
Auth0 by Okta takes a modern approach to customer identity and enables organizations to provide secure access to any application, for any user. Auth0 is a highly customizable platform that is as simple as development teams want, and as flexible as they need. Safeguarding billions of login transactions each month, Auth0 delivers convenience, privacy, and security so customers can focus on innovation. For more information, visit https://auth0.com.
About the author

Diego Poza
Sr Manager, Developer Advocacy (Auth0 Alumni)