Every six months, we compile a list of the worst data breaches that occurred during that period in order to learn from them. So far this year, the causes of the worst data breaches have shifted from human error and credential based attacks that we saw at the end of last year to ransomware, third-party vulnerabilities, and undetected security gaps.
This suggests that threat vectors may be changing, and organizations would be wise to bolster their cybersecurity efforts against new ways cybercriminals are now gaining access to data.
Below, we break down 10 of the worst data breaches in 2021 so far, as well as what organizations can learn from those breaches.
1. Over 30K Organizations Exposed in Microsoft Breach
On March 2nd, 2021, Microsoft reported it was the victim of a state-sponsored cyberattack from the Chinese hacking group called Hafnium. Microsoft explained in their notification that the group “primarily targets entities in the United States for the purpose of exfiltrating information from a number of industry sectors.”
The attack affected over 30,000 organizations across the United States, including local governments, government agencies, and businesses. It is the eighth instance of a nation-state cyberattack against civil organizations and businesses Microsoft has reported in the last 12 months.
How the Breach Occurred
The Microsoft breach was carried out through a sophisticated zero-day hacking campaign that targeted hundreds of thousands of on-premise servers running Microsoft’s Exchange software. Hafnium gained access to on-premise servers through a combination of stolen passwords and previously undetected vulnerabilities. Then, Hafnium created a web shell around those servers that provided them with the access they needed to steal email data remotely.
What Data Was Exposed
Microsoft’s Exchange Server software handles email communications, and the attack exposed the emails of each organization.
The Lesson for Businesses
Keep on-premise third-party software up to date at all times.
Hafnium was able to carry out this attack because of undiscovered vulnerabilities in Microsoft’s software. Although Microsoft released patches designed to correct these vulnerabilities, their customers are still at risk unless they update their software with those patches:
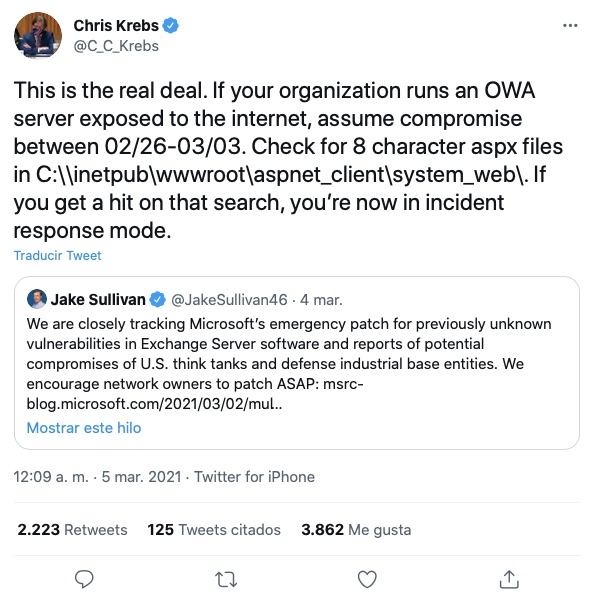
Source: Twitter
2. More Than 220M Brazilians Exposed in Major Data Leak
On January 19th, 2021, security researchers found highly sensitive personal data of over 220M Brazilians for sale online, a number that is greater than the current population of Brazil. The data also included detailed information on over 104 automobiles and 40M companies.
How the Breach Occurred
It’s unclear exactly how this data breach occurred. The nature of the data suggests it could have originated from Serasa, the Brazilian subsidiary of the credit bureau Experian. However, after an investigation, Serasa and Experian found no evidence that their systems had been compromised.
Brazilian consumer rights foundation Procon continues to investigate. “No hypothesis has been ruled out, and at the moment we consider it is more likely that the leak came from inside companies rather than hackers,” Fernando Capez, Procon’s executive director, explains.
What Data Was Exposed
The data leaked in this breach affected nearly all the Brazillian population and included personal tax identification numbers, birthdays, full names, addresses, headshots, credit scores, personal financial information, social benefits information, and more.
The Lesson for Businesses
Familiarize yourself with Brazil’s new privacy law and ensure your organization complies if it processes the data of any person within Brazil.
The unclear cause of this data breach makes it difficult to draw a concrete lesson. However, it’s worth noting that, regardless of what caused the breach, the consequences for the responsible organization are crystal clear now that Brazil’s new privacy law is in effect.
Like the EU’s GDPR, Brazil’s privacy law carries implications for businesses outside Brazil, as well as penalties up to USD $9M for non-compliance. If your business collects or processes the data of anyone who lives in or has visited Brazil, it’s worth familiarizing yourself with the law to ensure you’re in compliance.
3. Over 533M Facebook Users’ Personal Information Leaked
On April 3rd, 2021, hackers posted a database of over 533M Facebook users’ personal information online for free in a hacking forum. The data included information that could be used to identify individuals from 106 different countries, with the US, the UK, and India experiencing the greatest numbers of exposed records.
How the Breach Occurred
Facebook reported cybercriminals scraped data from their servers using a misconfiguration in their contact importer.
What Data Was Exposed
The leaked database contained personal information such as phone numbers, Facebook IDs, names, birthdays, and even some email addresses that could be used to carry out social engineering attacks on individuals on a large scale in the future.
The Lesson for Businesses
Find and fix misconfigurations before cybercriminals do.
Verizon's 2020 Data Breach Report found that misconfiguration errors similar to that which caused this year’s Facebook breach have increased since 2015:
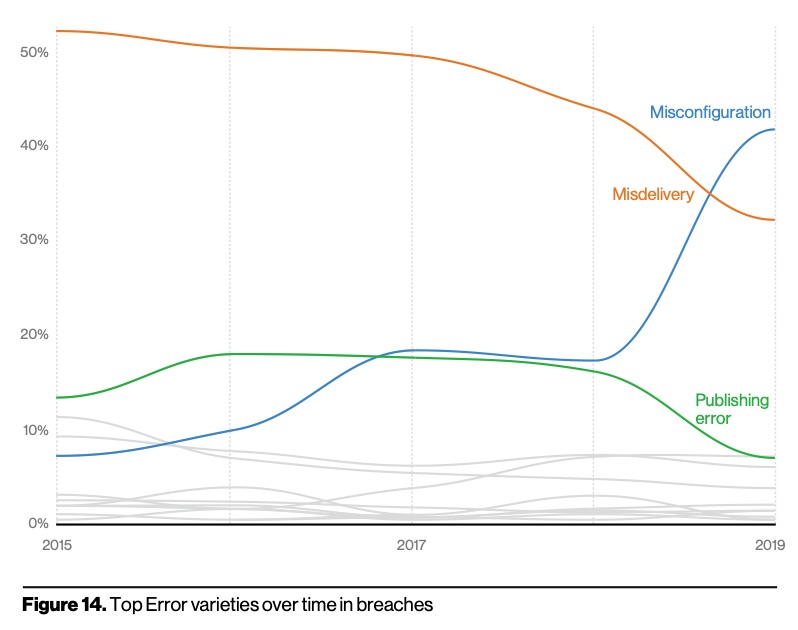
Verizon’s report also acknowledged the majority of these misconfigurations are discovered by security researchers rather than cybercriminals. However, the Facebook breach is a reminder to every organization that auditing and testing their systems for vulnerabilities is a worthwhile investment.
4. 17 Organizations Affected in Accellion Data Breach (So Far)
In December 2020, file transfer and collaboration software provider Accellion discovered a zero-day vulnerability in their File Transfer Appliance (FTA), a file sharing service they acknowledged was at the end of its life and released a patch to fix it. In January, they released four additional patches to address other vulnerabilities that bad actors used to attack their customers through their FTA service.
However, before 17 of their customers could install the patch, ransomware group Clop and financial crime group FIN11 exploited these vulnerabilities to access their data. Those organizations included The US Department of Health and Human Services, the University of California, and HealthNet.
Accellion now faces lawsuits in multiple US states over the breaches.
How the Breach Occurred
Bad actors used Structured Query Language (SQL) injection to deploy a web shell on servers using Accellion’s FTA system. This provided remote access they could use to steal information and remove traces of their access from system logs.
What Data Was Exposed
Accellion’s FTA system was designed for sending highly sensitive files. Although the nature of the information that passed through their software depended on the nature of their customers’ businesses, there was a strong likelihood that whatever bad actors gained access to was valuable.
The Lesson for Businesses
Update third-party software as soon as possible when a patch is made available.
The Accellion breach is a reminder that on-premise third-party software creates a vulnerability for organizations if it’s not kept up to date. When patches are released, ensure your software is updated immediately.
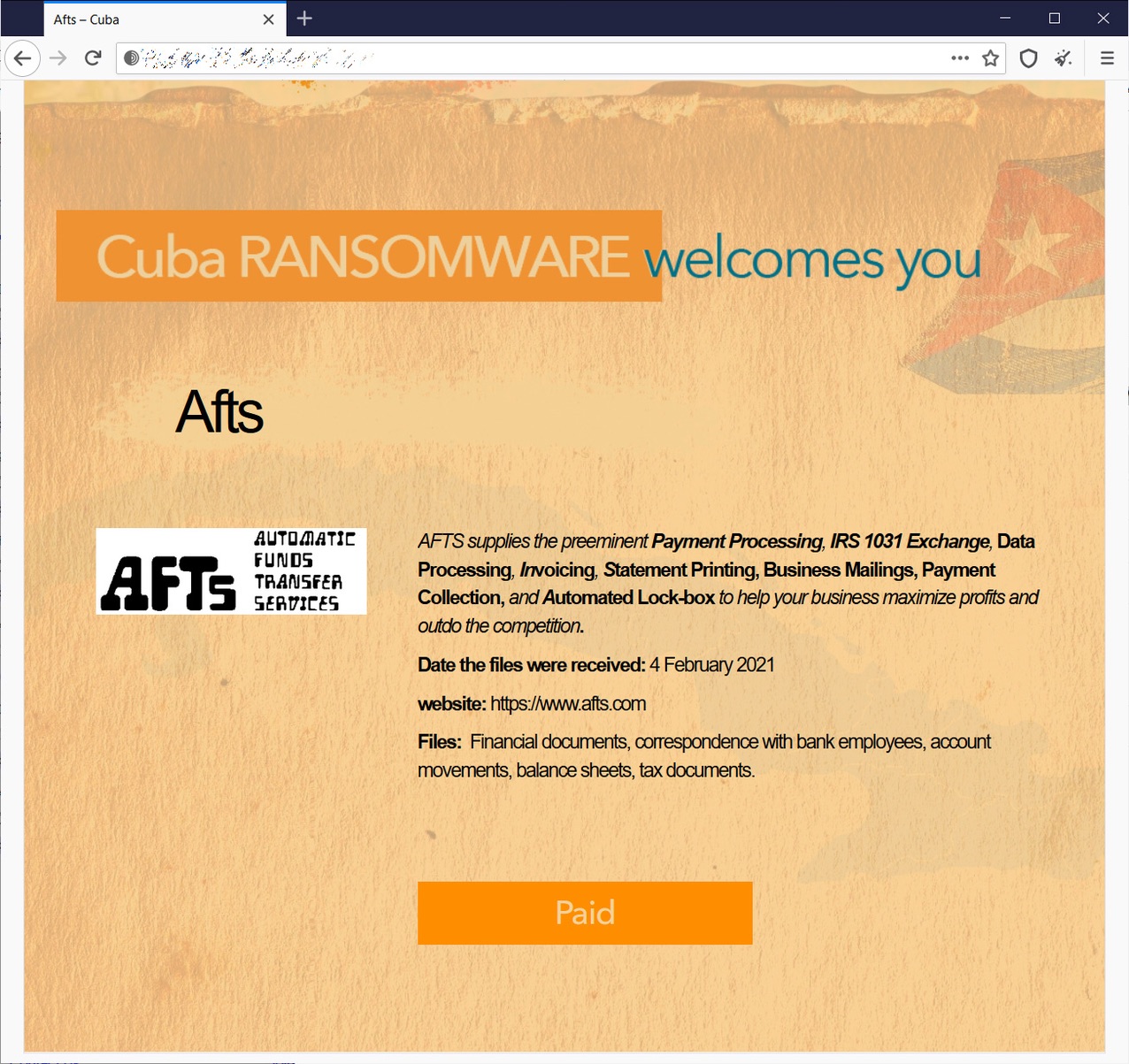
5. Millions Affected in Automatic Funds Transfer Systems (AFTS) Attack
Between February 3rd and 4th, 2021, third-party payment processor AFTS experienced a ransomware attack that led to a breach of millions of individuals’ data.
AFTS processes payments for local governments across North America, and the breach is estimated to have affected up to 38 million automobile owners in California alone. Multiple local governments and their agencies have also released notices explaining how the breach may affect their residents. A full list of cities and agencies affected can be found here.
The attack was carried out by Cuba Ransomware, a cyber gang responsible for numerous attacks on financial, logistics, and technology organizations across North America and Europe over the past few years.
How the Breach Occurred
At this time, it’s unclear how ransomware entered AFTS’s systems. However, ransomware is most commonly installed by visiting an infected website or via a phishing email.
What Data Was Exposed
According to Cuba Ransomware’s website page on the data breach, the files leaked included “financial documents, correspondence with bank employees, account movements, balance sheets, and tax documents.”
The Lesson for Businesses
Ransomware protection and third-party risk management should be a top priority.
According to a study by the Ponenon Institute and CyberGRX, at least 53% of organizations have had one or more data breaches caused by a third-party they work with. So like many of the other breaches on this list, the AFTS breach reinforces the need for both managing third-party risks and also protecting your organization against ransomware.
6. MeetMindful Breach Exposes 2.28M Users’ Data
On January 20th, 2021, a 1.2GB file containing personal data from 2.28M people who use MeetMindful’s online dating services was posted on a well-known hacking site. MeetMindful’s investigation concluded that the breach only affected users who had created or updated their accounts prior to March 2020.
How the Breach Occurred
MeetMindful found that cybercriminals were able to gain access to the data through a vulnerability in their system they have since resolved.
What Data Was Exposed
MeetMindful’s notice states that first names, email addresses, city and state location information, and notification preferences were all included in the file that was released. No payment or user-generated content (messages, photos, etc.) were leaked in the breach.
The Lesson for Businesses
Consider hiring ethical hackers to find vulnerabilities before cybercriminals do.
Cybercriminals are always looking for undetected security gaps they can use to access your systems and data. Many companies have found hiring ethical hackers helps them find those gaps before real cybercriminals do.
Even Basic Information Can Pose a Threat if Leaked
Several of the breaches on this list were limited to information many would not consider sensitive by nature. While it’s good that companies are taking steps to protect their most sensitive data, it’s also important to remember that a leak of basic information could still be damaging to those who depend on your organization.
For example, an email address and a name may not seem like sensitive data. But sometimes, those simple pieces of information are all it takes to create a phishing email that’s convincing enough to get someone to hand over something more sensitive.
It’s in every organization’s best interest to ensure all of their customers’ and employees’ data is protected from unauthorized access, no matter how basic it might seem. A breach at one organization could lead to a breach at another.
About the author

Jameeka Aaron
CISO
Jameeka has over 20 years of Information Technology and Cyber Security experience. She is a versatile leader, successfully leading teams as both a CISO and CIO across various industries including; Aerospace & Defense, Apparel, Retail, and Manufacturing at both Fortune 100 and privately held companies and many spaces in between.
She is highly skilled in Business Engagement (International and U.S. based) Audit, Compliance, Vulnerability, Risk and Identity Management, Digital Transformation, Mergers, Acquisitions, Divestitures, and leading Cross-Functional and Matrixed teams.