By Damien Guard
This document will help you troubleshoot your configuration if you get a 401 (Unauthorized) response from your API.We recommend that you log in to follow this quickstart with examples configured for your account. If you configured the JWT middleware correctly, you will be able to get proper responses from your API when you make requests. However, in the case where you get a 401 (Unauthorized) response from your API, it is because the configuration of your JWT middleware does not match with the JWT which was passed. This document will help you troubleshoot your JWT middleware configuration.How does a token get validated?
In terms of validating a JWT, there are various things to consider:- Is the token well-formed? In other words, is this token conforming to the structure of a JSON Web Token (JWT)? To get more information on the structure of a JWT, please refer to this section on the structure of a JWT
- Has the token been tampered with? The last part of a JWT is the signature. The signature is used to verify that the token was in fact signed by the sender and not altered in any way.
-
Has the token been received in its validity period? JWTs are only valid for a specified time period (as expressed in the
expclaim). -
Is the token coming from the intended Authority? This consists of 2 parts
- Signature Verification: Can we confirm that the JWT is correctly signed using the key issued by the issuing authority?
- Issuer Value: The Issuer is defined in the
issclaim. Once again does this claim match up with what your application expects?
-
Is the token intended for the current application? So does the
audclaim of the JWT match with what your application is expecting?
Inspecting a token
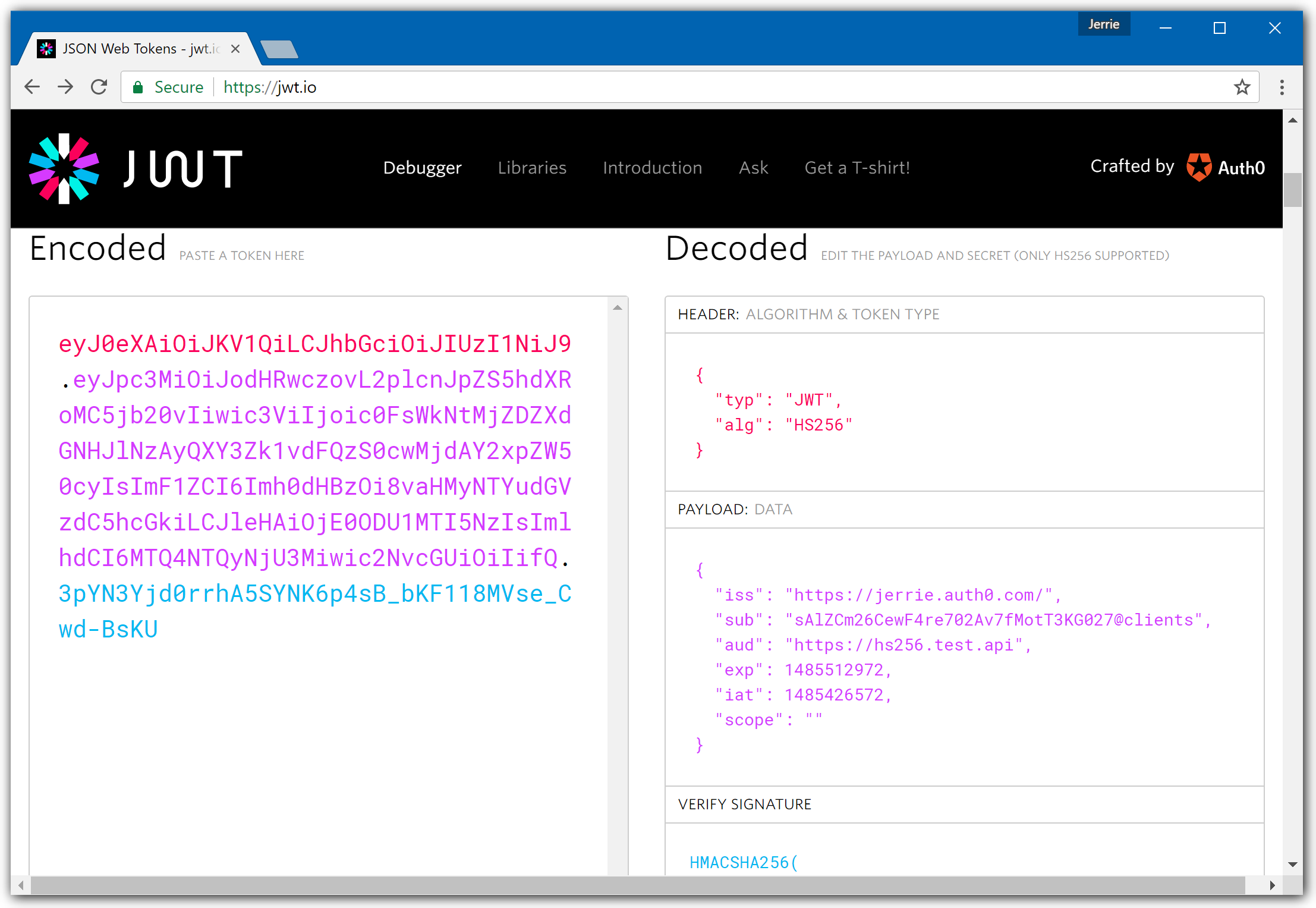
A quick way to inspect a JWT is by using the JWT.io website. It has a handy debugger which allows you to quickly check that a JWT is well-formed, and also inspect the values of the various claims.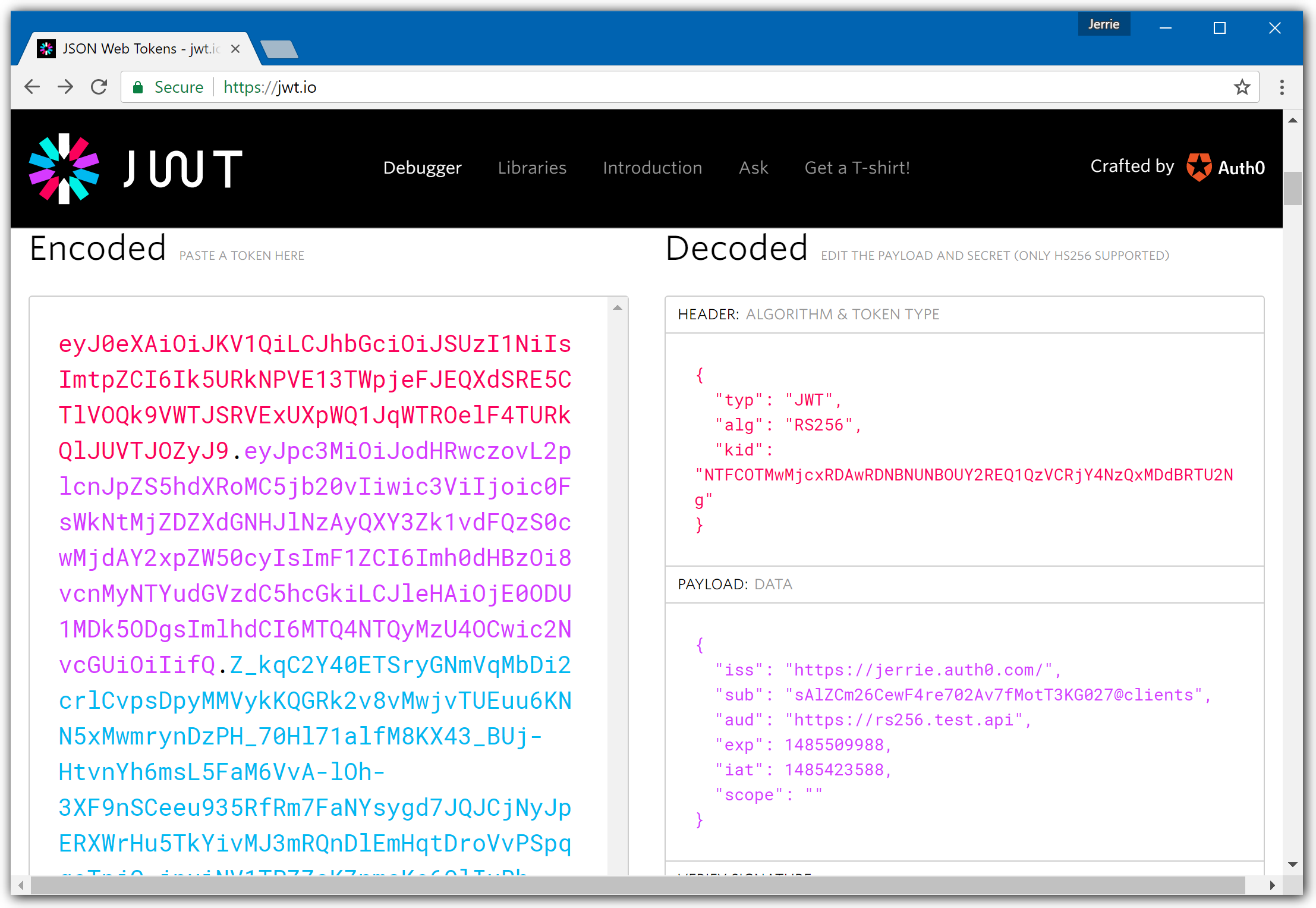
Using the log files to debug configuration issues
In order to inspect the log message which are generated by the OWIN middleware, you need to set the logging level to Verbose. So in yourweb.config file, add the following:
1. Are you actually passing the JWT in the Authorization header?
The first thing is to ensure that you actually pass along the JWT as a Bearer token in the Authorization header of the request. If you get a 401 (Unauthorized) response from your Web API, but you do not see any other error messages being logged to the Output Window, then most likely you are simply not sending the JWT in the Authorization header of the request. To resolve this issue, ensure that you send the JWT as a bearer token in the Authorization header.2. Did you configure the JWT middleware for the correct signing algorithm?
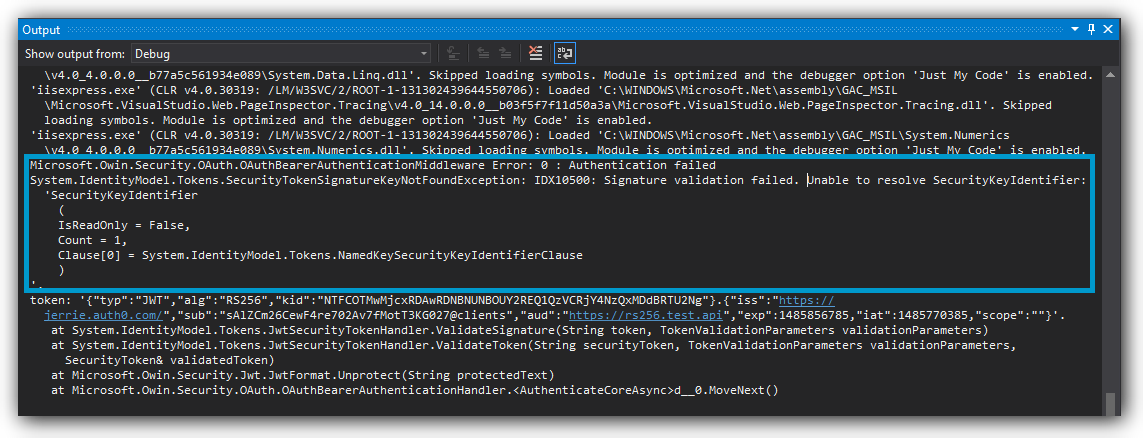
Another common mistake is that your tokens are signed using the HS256 signing algorithm, but your middleware is configured for RS256 - or vice versa. In the following screenshot, you can see that we get an error message that the signature validation failed. This is because the JWT middleware was configured to handle tokens signed using RS256, but instead, a token was sent which was signed using HS256.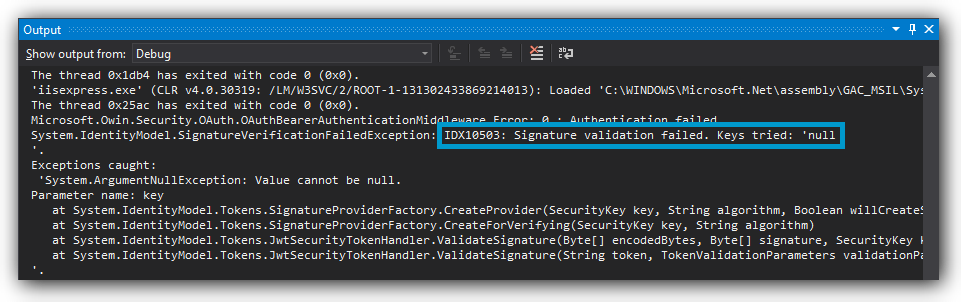
3. Has your token expired?
Each JSON Web Token is only valid until the time specified in theexp claim. If you and send a token which has expired, the token will be rejected:
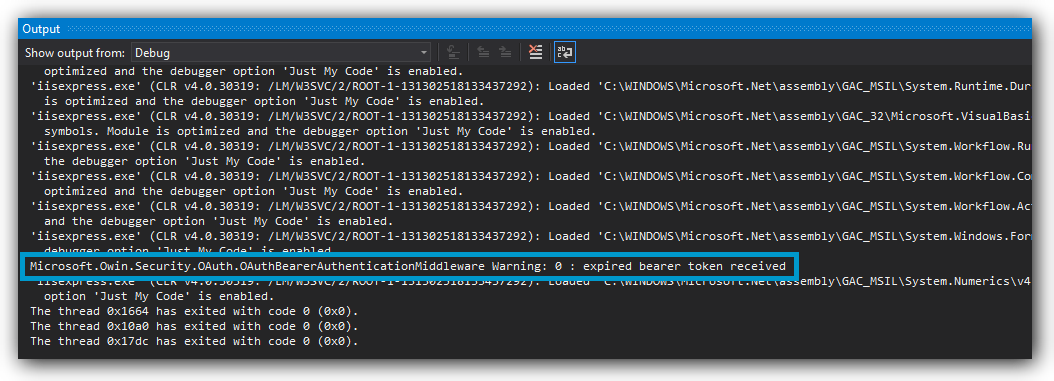
exp
The value of theexp claim is a numeric value representing the number of seconds from 1970-01-01T00:00:00Z UTC until the specified UTC date/time. If you want to see the actual date/time for the value, you can visit EpochConverter.
4. Did you configure the correct Issuer?
The Issuer specified in your token must match exactly with what is configured in your JWT middleware.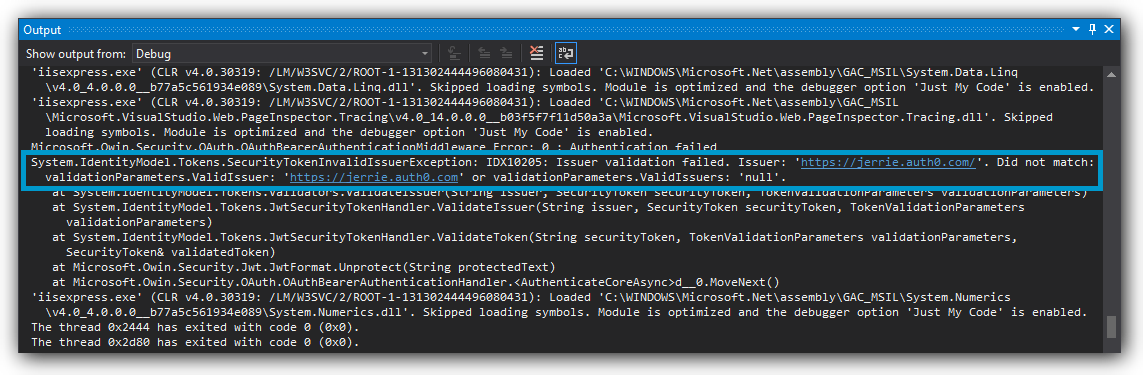
TokenValidationParameters.ValidIssuer property of the JwtBearerAuthenticationOptions parameter passed when calling app.UseJwtBearerAuthentication(...).
If your middleware is configured for HS256 signed tokens, this means ensuring that you have passed the correct value to the constructor of SymmetricKeyIssuerSecurityTokenProvider which was configured as one of the IssuerSecurityTokenProviders for the JwtBearerAuthenticationOptions.
5. Does the audience match?
The audience specified in your token must match exactly with what is configured in your JWT middleware.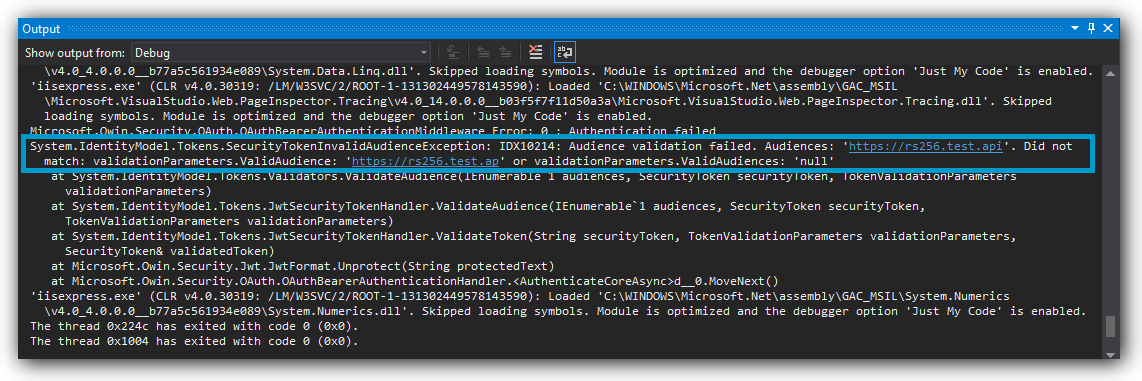
ValidAudience property of the TokenValidationParameters
If your middleware is configured for HS256 signed tokens, this means ensuring that you have added the correct audience to the list of AllowedAudiences for the JwtBearerAuthenticationOptions.
Edit on GitHub
