同意ダイアログ
ユーザーがサードパーティアプリケーションを通じて認証を行い、そのアプリケーションがユーザー情報へのアクセスや、代理としてAPIで何らかのアクションを行うことへの認可を求める場合、ユーザーに対して同意ダイアログが表示されます。 たとえば、このような要求: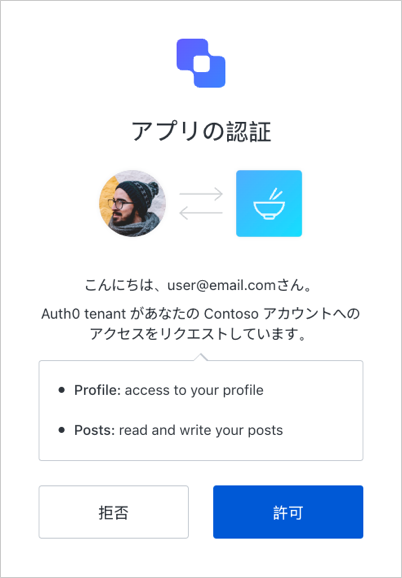
スコープの説明
デフォルトでは、同意ページは、スコープの名前を使ってユーザーの同意を求めます。下の図のように、スコープ名を action:resource_name 形式で定義します。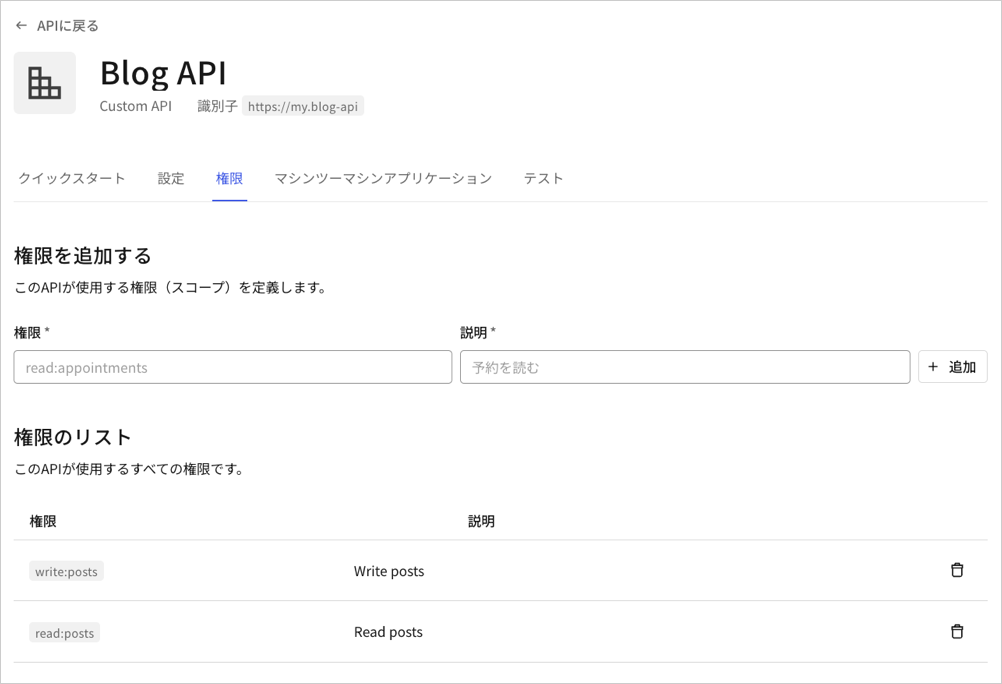
拒否された許可に対処する
ユーザーがアプリケーションへの同意を拒否した場合は、要求の中で指定されたredirect_uriに、access_deniedエラーと共にリダイレクトされます。
ファーストパーティアプリケーションに対して同意をスキップする
ファーストパーティアプリケーションは、同意ダイアログをスキップできますが、これはユーザーの代わりにアクセスしようとしているAPIの [Allow Skipping User Consent(ユーザー同意のスキップの許可)] オプションが有効になっている場合にのみ可能です。ユーザーの同意とアプリケーション
現時点では、検証可能なファーストパーティアプリケーションのみが同意ダイアログをスキップできます。
localhostは検証可能なファーストパーティーになり得ない(ユーザーが悪意のあるアプリケーションをlocalhostで実行する可能性がある)ため、ファーストパーティーアプリケーションであるかにかかわらず、localhostで実行されるアプリケーションには常に同意ダイアログが表示されます。開発中には、以下のようなエントリーを/etc/hostsファイルに追加すると、これを回避することができます。127.0.0.1 myapp.example同様に、「localhost」がアプリケーションの Allowed Callback URLs(許可されているコールバックURL) 設定([Dashboard]>[Applications(アプリケーション)]>[Settings(設定)])にあるいずれかのドメインに含まれている場合、(ファーストパーティーアプリケーションであっても)同意はスキップできません。必ず、 Allowed Callback URLs(許可されているコールバックURL) を更新して、アプリケーションに構成したコールバックURLと更新後のドメインマッピングが一致するようにしてください。同意を取り消す
リソース所有者のパスワードフローを使うときは、同意ダイアログは使用されません。ユーザーが直接アプリケーションにパスワードを入力し、これがアプリケーションに対してユーザーアカウントへのフルアクセスを付与したことと同じになるためです。- [Auth0 Dashboard]>[User Management(ユーザー管理]>[Users(ユーザー)]に移動し、同意を取り消すユーザーをクリックします。
- [Authorized Application(認可アプリケーション)] タブをクリックします。
- 該当するアプリケーションの横にある [Revoke(取り消し)] をクリックします。
パスワードベースのフロー
/authorizeエンドポイントにリダイレクトするときにprompt=consentパラメーターを含めることで、ユーザーに対して同意を強制できます。これは、ユーザーにアプリケーションと要求されたスコープに対するユーザー付与がすでにある場合でも同じです。

