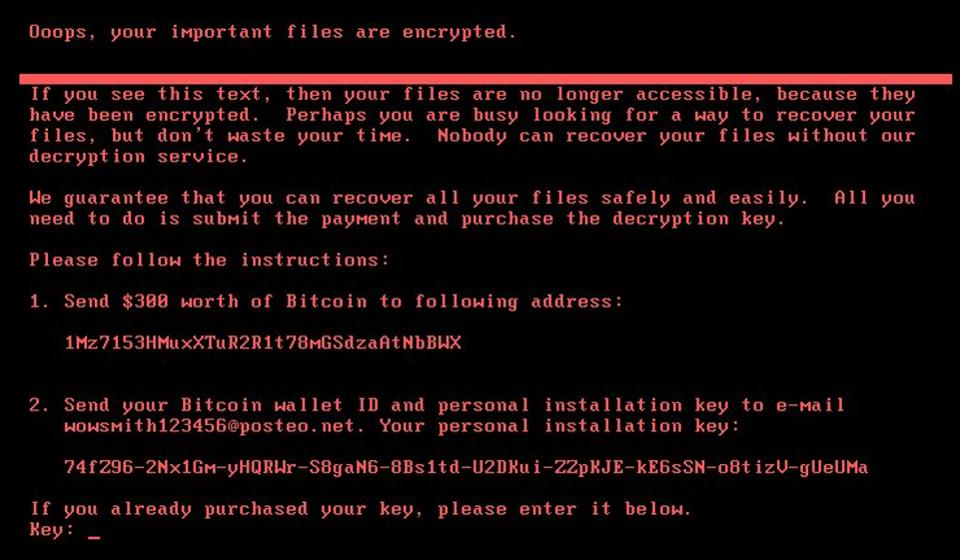
In May, a ransomware called WannaCry became famous around the world for holding computers' file systems as hostages. Today, government institutions (like Ukraine's national bank) and companies from the private sector reported that another outbreak has started.
The ransomware responsible for haunting organizations today is called Petya, although this name originates from a ransomware that attacked last year. Similarly to WannyCry, today's Petya ransomware starts by encrypting a computers file systems and then it demands payments to restore access to these files.
What Is a Ransomware?
The very definition of ransomware is a malware that blocks access to the victim's data until a ransom is paid. There are some ransomwares that lock the systems in a way that is not difficult to reverse, but the more advanced ones are using a technique called cryptoviral extortion. This technique consists of encrypting victims files, makes them inaccessible. To regain access, the authors demand a ransom payment to reverse the encryption. Nowadays, most ransomwares are requesting Bitcoins as ransom payment, to take advantage of cryptocurrency's anonymity.
What Is Petya Ransomware?
The real name of the ransomware that is striking today has not been defined. But, as this ransomware is supposed to be a variant of Petya, the name is being reused. Petya locks a computers hard drive as well as individual files stored on it. It's not easy to recover data from the computers affected by this malware.
One interesting fact is that cyber security experts at Kaspersky Lab have released a report that said the ransomware was not related to Petya but was in fact a new ransomware it called NotPetya. The contradictions are yet to be clarified.
How Petya Started?
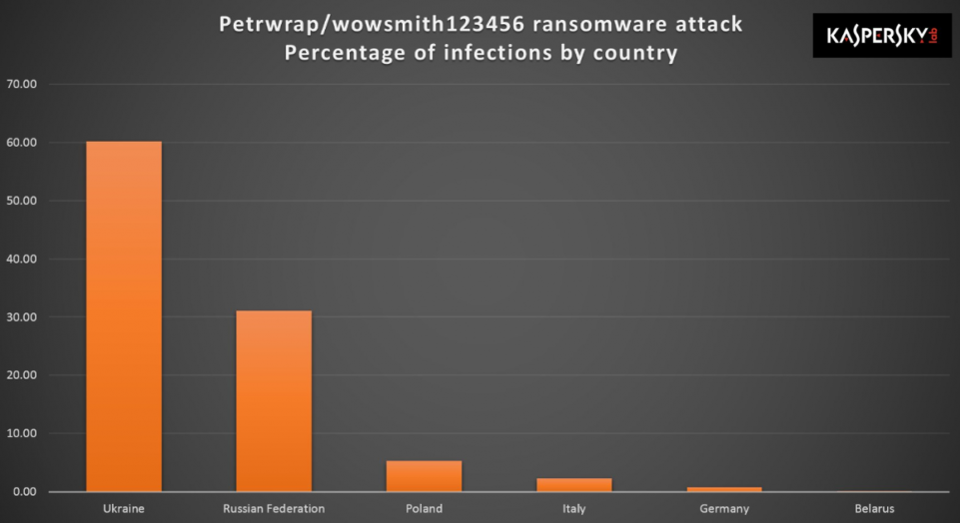
A Ukrainian software firm is alleged to be the source of today's outbreak. Although there is no confirmation about this, and that the company has denied these claims in a Facebook post, the outbreak is indeed striking Ukraine harder then any country.
How The Petya Ransomware Spreads?
Researchers are saying that the this new outbreak is hitting systems via the same leaked NSA vulnerabilities used by WannaCry. The analysis of some of Petya's samples confirmed that the malware author used the EternalBlue exploits, which targeted a vulnerability in Microsoft Windows. Microsoft already created patches to solve EternalBlue vulnerability, but many computers out there don't have this patch applied.
How Do I Protect Myself?
Although no solutions were found for retrieving data from computers affected by Petya so far, you can review and update your devices and also check that your approach to security is good. Recently we wrote a blog post that shares some good practices regarding Personal Information Security Guide for Family and Friends.
Be sure to check out this guide to learn how to secure your wireless network, backup your data so that it is not lost if you become a victim of ransomware such as WannaCry, detect phishing scams, and more.
Aside: Securing Applications with Auth0
Are you building a B2C, B2B, or B2E tool? Auth0, can help you focus on what matters the most to you, the special features of your product. Auth0 can improve your product's security with state-of-the-art features like passwordless, breached password surveillance, and multifactor authentication.
We offer a generous free tier so you can get started with modern authentication.
About the author

Bruno Krebs
R&D Content Architect (Auth0 Alumni)