Discover when requests to a tenant are rate-limited
There are a handful of ways to determine if a customer product is being rate limited by Auth0. See below for the possible causes of rate limitation.Tenant logs
By subscribing to different tenant logs, you can track issues related to request volumes. To understand how tenant and operations event logs work in Auth0, read Logs.api_limit
Theapi_limit event is triggered immediately after a rate limit is exceeded for the global rate limit bucket for the Authentication or . If the number of request tokens utilized remains above 80% after one minute for the same rate limit bucket, a second warning log is generated. If a rate limit is exceeded for a different rate limit bucket, a new api_limit event is generated. This helps customers identify which rate limit configuration their API calls are triggering, which is a critical first step in diagnosing the root cause.
api_limit_warning
Theapi_limit_warning log is triggered when a customer’s request rate consumes 80% of the request tokens for a given rate limit bucket. If the number of request tokens utilized remains above 80% after one minute for the same rate limit bucket, a second warning log is generated. If the 80% threshold is exceeded for a different rate limit bucket, a new api_limit_warning log is created.
appi (Public Performance Burst Only)
Theappi log is triggered when a customer tenant with a Public Performance Burst add-on exceeds their sustained Authentication API request rate limit of 100 RPS, consuming a 15-minute block of their 48-hour burst allocation. If, after 15 minutes, the request rate exceeds the 100 RPS sustained request limit again, a second appi log will be triggered.
API responses
Auth0 API responses deliver HTTP 429 (Too Many Requests) responses with the exceeded rate limit. This enables customers to observe rate limit enforcement in real time. However, this is only useful for custom-built customer applications interacting directly with the Auth0 API.SDK error handling
If you are using an SDK, refer to the Management API SDK libraries error pages.Error pages
The error page response is sent for endpoints that render HTML content to the end user. If your tenant is configured to use generic (Auth0 hosted) pages, Auth0 renders the error page instead of the expected content when you exceed the response limit. If your tenant is configured to use custom error pages, the user is redirected to the custom error page URL with the relevant error in theerror_description query string parameter. For more information, see Affected endpoints and the JSON Error descriptions.
Find out why a tenant is being rate limited
If you believe tenant requests are rate limited and need assistance to understand why, open a request via the Support Center. As part of your request, please include the full raw log where the issue was seen.Predict when requests to a tenant will be rate limited
Auth0 reports up-to-date information on the current status of your rate limits using HTTP response headers from endpoints that have rate limit policies configured. This status is communicated as follows:x-ratelimit-limit: Maximum number of requests available.x-ratelimit-remaining: Number of remaining requests available until the bucket is refilled with additional requests.x-ratelimit-reset: UNIX timestamp, in seconds, of the expected time when additional requests will be added to the bucket.
- Burst Limit:
1000 - Sustained Rate Limit:
100requests per second(on a fixed window)
- The sustained rate limit is
100 requests per secondon a fixed window. - Due to the fixed window, the bucket of requests is refilled every second.
x-ratelimit-limit: 1000x-ratelimit-remaining: 50x-ratelimit-reset: 1675452600
- Your tenant has used up 950 of the 1000 requests allowable to that API, and only has 50 requests remaining until such time that additional requests are added.
- New requests will be added at
1675452600, or 7:30:00 PM UTC on February 3, 2023. - 1 new request will be added at that time
Examples of how rate limits are enforced
Requests per second example
Assume Auth0 launches a new API called/ratelimitexample with the following rate limit values:
- Burst limit: Five (5) requests
- Sustained rate limit: 10 requests per second.
- API begins with, and will never exceed, five request tokens, which is equal to the burst limit.
- The bucket of 10 tokens is refilled every second, using a “fixed window.” New tokens are added to the bucket, refilling it at the “top” of each second.
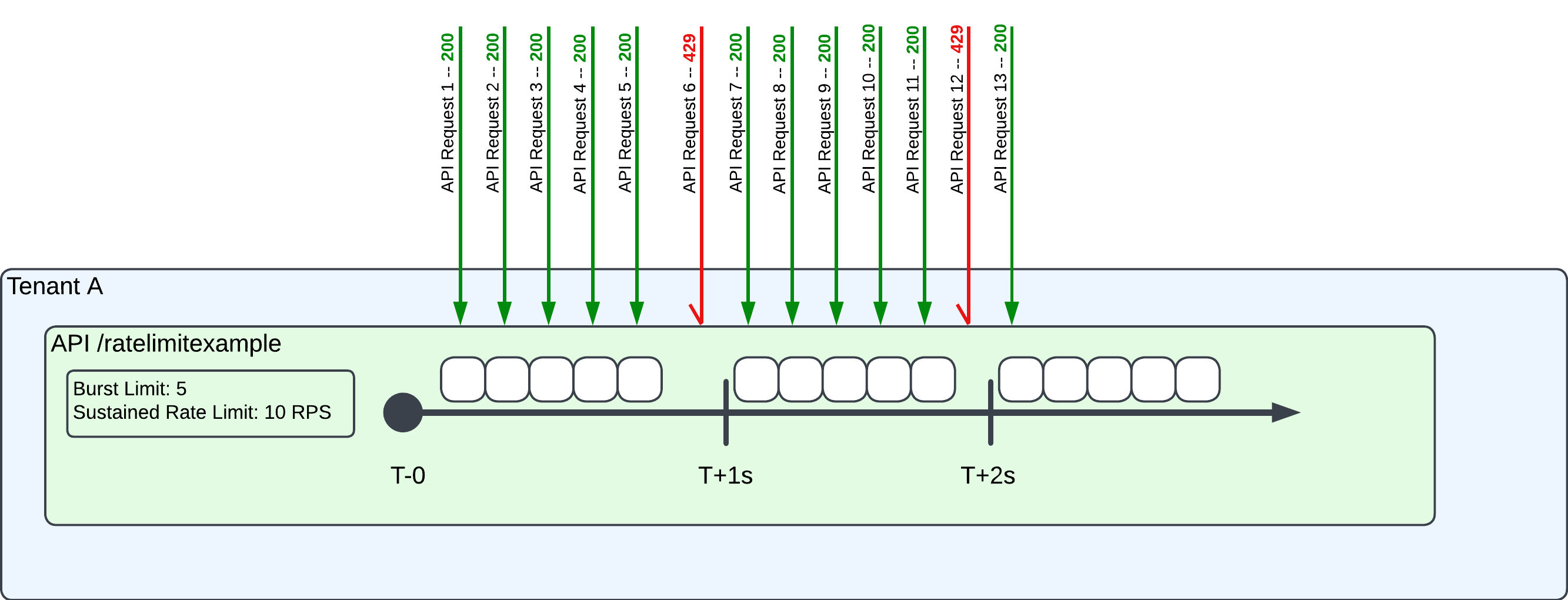
- T0 - T1sec: The end user makes six requests in the first second. Five requests – equal to the burst limit – receive a
200response. The sixth request receives a429error because there are no remaining request tokens in the bucket. - T1sec - T2sec: Auth0 tops off the bucket of request tokens because of the fixed window algorithm. As a result, the seventh through 11th requests are successful, exhausting the bucket by the 12th request, resulting in a
429error. - T2sec - T3sec: Auth0 refills the token bucket once again, and the next request (13) receives a
200response.
Requests per minute example
Assume Auth0 launches a new API called/ratelimitexample2 with the following rate limit values:
- Burst limit: Five (5) requests
- Sustained Rate limit: Six (6) requests per minute.
- API begins with five request tokens, which is equal to the burst limit.
- The bucket of six tokens is refilled every minute, using a “fixed window.” New tokens are added to the bucket, refilling the it at the “top” of each minute.
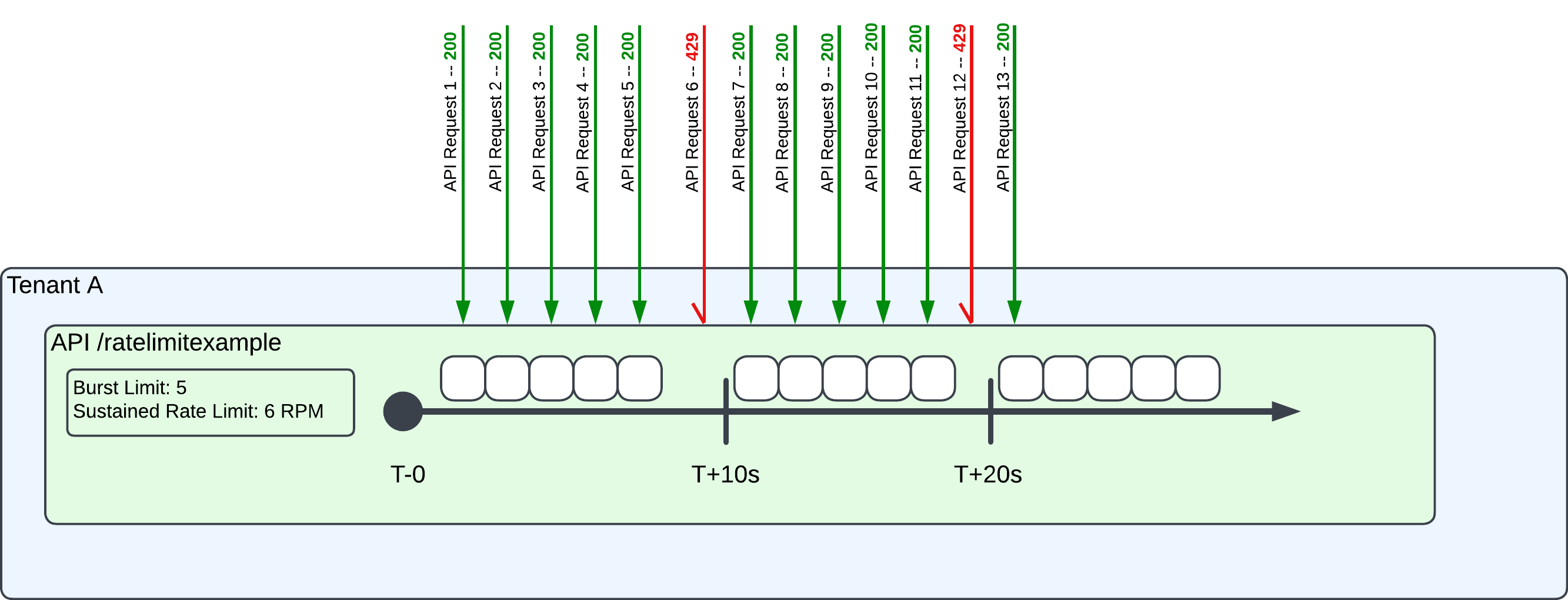
- T0 - T+1min: The end user makes six requests in the first minute. Five requests – equal to the burst limit – receive a
200response. The sixth request receives a429error because there are no remaining request tokens. - T+1min - T+2min: Auth0 refills the token bucket because of the fixed window algorithm. As a result, the seventh through 11th requests are successful, exhausting the bucket by the 12th request, resulting in a
429error. - T+2min: Auth0 refills the token bucket once again, and the next request (13) receives a
200response.
Other scenarios
On occasion, Auth0 will assign two rate limits to a single API. This is done in order to configure a burst limit and the sustained rate limit that is more customized to the needs of the service. In effect, the first rate limit becomes the effective burst limit, and the second rate limit becomes the effective sustained rate limit. In this scenario, Auth0 only publishes the effective burst and sustained rate limits, rather than communicating the actual burst and sustained rate limits.End-user Login and Signup API usage
There are a handful of Authentication Flows, including Login, Signup and Change Password. The most common of these are typically Login, followed by Signup. An end user’s login initiates multiple API calls to Authentication API endpoints in order to determine if the end user is authorized to receive an Authorization token, and thereby access the application they have requested. The precise number of API calls is a function of a handful of configurations:- Authentication Experience (e.g., New or Classic Login)
- Authentication Flow (e.g., Login, Signup, or Change Password)
- Authentication Flow Type (e.g., Login via Username / Password; Login via Social Login; Login when an existing Authentication Token already exists)
Universal Login
Auth0 Universal Login provides the essential feature of an : the login flow. When a user needs to prove their identity to gain access to your application, you can redirect them to Universal Login and let Auth0 handle the authentication process.| Authentication flow | Flow type | Requests to Authentication API endpoints |
|---|---|---|
| Login | Username/Password Challenge* | 5 |
| Login | 3rd Party Identity Provider – e.g., Social or Work Login | 6 |
| Login | Auth0 Authentication Session Exists | 1 |
| Signup | via Username/Password | 6 |
Modifiers
Certain authentication configurations modify the base request count. These adjustments depend on additional security measures or authentication flows:| Modifier | Description | Additional Requests |
|---|---|---|
| ID First | Identifies the user before requesting credentials. | +2 |
| MFA | Adds Multi-Factor Authentication. | +2 per factor |
| OTP | One-time password for Authentication | +2 |
| Enterprise Login | Authentication through an enterprise connection (e.g., SAML, OIDC, LDAP). | +1 |
| Client Credentials | Used for machine-to-machine authentication. Applies universally, even if actions are used. | +1 |
Classic login
Classic Login is an Auth0-hosted login experience that relies on JavaScript for customization. Implementing Classic Login is less complex than embedding the authentication process directly in your app, and can help prevent the dangers of cross-origin authentication.| Authentication flow | Flow type | Requests |
|---|---|---|
| Login | Username/password challenge | 8 |
| Login | 3rd Party Identity Provider – e.g., Social or Work Login | 8 |
| Login | Auth0 authentication session exists | 2 |
| Signup | Username/password | 8 |
Modifiers
The following factors increase request counts for Classic Login:| Modifier | Description | Additional Requests |
|---|---|---|
| SMS Authentication Only | When using SMS as the primary authentication method. | +7 |
| Native Social Login | Login using a native social provider (e.g., Google, Facebook). | +1 |
| Redirects | Additional redirects during authentication increase request count. | +1 |

